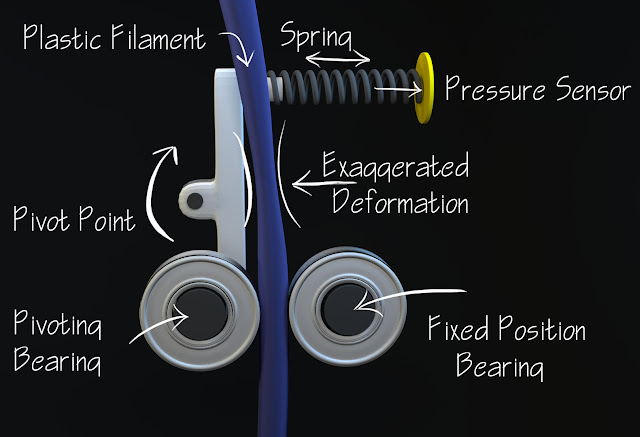
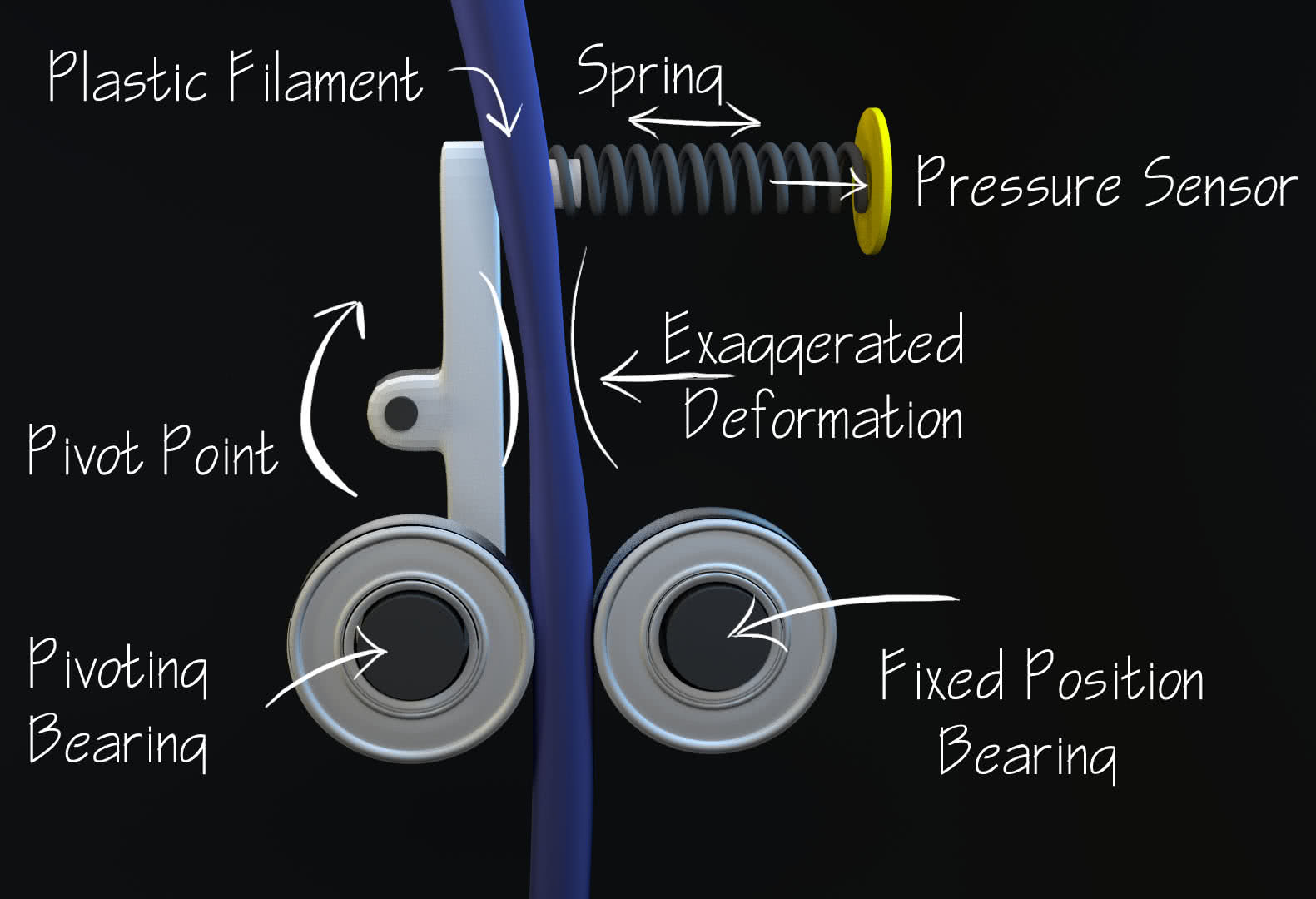
Concept for Real Time Filament Measurement
 |
| Filament diameter effects on a print |
The idea to measure the diameter is simple. It uses a pivot, a few bearings, a spring, and a pressure sensor. As the filament diameter fluctuates, the bearing assembly pivots causing the spring to place more or less pressure on the sensor. We can relate the pressure directly to the amount of movement of the print. This is very predictable since spring forces are linear with regard to changes in length. Since we know the diameter, we can scale our extrusion amount accordingly.
Since must of 3D printing is open loop, that is to say there is no feedback, this measurement of filament provides the last bit of information the system needs. Here’s a simple example of a print that had a change in filament diameter. You can see the outer parameters are consistent, but when filling in the bottom the width of the extrusion changes.
<div class="separator" style="clear: both; text-align: center;"></div>